| Warnings: |
When opening existing model files that were prepared by older versions of OrcaFlex, beware of compatibility issues for data files. Binary data files have strong version compatibility features, but text data files do not. Because of this we recommend that you use the binary data file to transfer models between different program versions. The convert text data files tool can be used to ease this process. |
|
|
When performing restart analyses, beware of compatibility issues if the parent model was run in a different version of OrcaFlex. The best practice is to run both parent and child models in the latest available version of OrcaFlex. |
A more in depth discussion of the major new features introduced in 11.6 is available on our blog.
New in version 11.6c
Line setup wizard
The line setup wizard has exposed a new convergence parameter named delta. This determines the size of perturbation when calculating the Jacobian by perturbation. This value should be chosen to be larger than the statics convergence tolerance. In previous versions this value existed, but was hard-coded to be 1e-8 which for some models is too small. When loading models initially created in older versions, this value of 1e-8 is preserved, and you may need to increase it to, for example, the new default value of 1e-4.
Shaded graphics
The shaded sea surface now only resamples the sea surface $Z$ when necessary. This should increase performance navigating the shaded model when the simulation is not running or replaying.
Bug fixes
These bugs are fixed in version 11.6c.
New in version 11.6b
User interface
Bug fixes
- Importing a 3D model which includes lines or points would fail with a shaded graphics error being reported. Lines or points in a 3D model should be ignored when imported into OrcaFlex.
- The drawing page of the general data form could sometimes display some empty view parameter controls that should have remained hidden.
- Attempts to evaluate user defined results for constraints in frequency domain analyses failed with an unexpected program error.
- Shadows on the shaded sea surface would render lighter instead of darker when the viewer was underwater.
- The OrcaFlex code to register user defined results (UDR) variables did not check the validity of the units string provided by the UDR. For some result types this would lead to an unexpected program error being reported.
- On some computers, clicking a boolean cell in a grid control would lead to an unexpected program error being reported.
- The shaded projection mode, introduced in 11.6a, could not be specified in the API. This can now be specified as a member of the TViewParameters structure, and the analagous structures for Python and MATLAB.
These bugs are fixed in version 11.6b.
New in version 11.6a
Shaded graphics
- The shaded graphics functionality has been re-implemented using DirectX 12 and now takes a physically based rendering (PBR) approach.
- The sea surface, seabed, and sky are drawn with advanced lighting models and allow greater customisation from the environment drawing page.
- Shadows are cast by objects in the scene according to the sun position and can add depth and realism to the rendering.
- The underwater POV simulates the natural absorption and scattering of light that occurs when the viewer is underwater.
- A new view parameter projection mode, has been added, which can be set to either perspective or parallel. The new parallel option may be of use when switching between wire frame and shaded mode to preserve your viewpoint.
- The import of 3D models has been re-implemented using the Open Asset Importer Library (Assimp). In particular this means that Wavefront
.obj files are imported more faithfully. Additionally, this opens up future possibilities for OrcaFlex to import 3D models from other file formats supported by Assimp.
Frequency domain
Lines
- For line results which depend on radial position (e.g. stress components), you can now directly specify the radius for which results are reported. Previously such results were available at inner, outer and mid-wall locations. This functionality is available for results extracted in the GUI, from the API, for fatigue analysis, and for results extracted using the Excel post-processing sheet.
- The line segment pen can now, optionally, be specified by line section. This new option is in addition to the previously available options for defining the segment pen: by line type or by a single pen for the whole line.
- A new result variable, horizontal end force, has been added. This is the magnitude of the 2-vector whose components are end GX force and end GY force.
- The line properties report now allows you to specify a reference contents density. If the reference contents density is specified, then the properties report will be calculated assuming the contents have that density. If a value of '~' is used for reference contents density, then the properties will be calculated assuming the contents have the nominal density.
- The seabed span page of the summary results now reports maximum curvature and minimum bend radius for each span.
- Minimum bend radius variable data sources can now be modified after a calculation has been performed. Previously it was only possible to modify the minimum bend radius data specified on the line type data form, but now that flexibility has been extended to cover the variable data sources.
Constraints
Applied loads
Applied loads can now be specified via Python variable data, allowing forces and moments to be defined directly as mathematical functions of simulation time and (where appropriate) line arc length.
Variable data
Time history variable data sources (e.g. applied loads, winch payout rate, etc.) can now be specified in an external file, in addition to the existing option of being embedded directly in the data.
Wire frame data
Wire frame drawing data for vessels, vessel types, lumped 6D buoys and wire frame shapes can now be specified by an external panel mesh file. This option is in addition to the existing option of the wire frame data being embedded directly in the model data. If the same wire frame data is used for many different model files, e.g. different load cases, then keeping the wire frame data as an external file can reduce file storage requirements. Another benefit is that there are no limits placed on the number of vertices and panels that define the wire frame. There are such limits when the data are stored internally, for reasons of file format compatibility.
Environment
- 3D seabed data can now be specified in an external file, in addition to the existing option of being embedded directly in the data.
- Users can now directly specify the nominal depth used when evaluating wave theory calculations and current vertical stretching. Previously, these calculations were always based on the water depth at the seabed origin.
Line setup wizard
The line setup wizard has been generalised to allow arbitrary line results variables (including user defined results) to be used as targets. Previously only a limited number of pre-determined variables could be used. As a consequence of this, existing automation scripts may need to be updated.
Move selected objects wizard
The move selected objects wizard can now rotate objects around an arbitrary axis. Previously the only rotation that was possible was rotation in the horizontal plane.
Compound object properties
The compound object properties report now includes wetted volume and centre of wetted volume. These properties are reported using the instantaneous object positions (in the current model state), and can account for partial submergence. However, other properties that are related to volume and buoyancy are reported assuming complete submergence, as in previous versions of OrcaFlex.
Turbines
Fatigue analysis
For rainflow fatigue, the way damage rate (= load case damage / sample duration) is calculated has been changed very slightly. The change is in how the sample duration is calculated. Previously the sample duration was taken as the time between first and last extrema in the response variable time history. Now the sample duration is taken to be the total sample duration, i.e. $T_\textrm{to} - T_\textrm{from}$ where $T_\textrm{from}$ and $T_\textrm{to}$ define the simulation period as specified in the load case table.
This change will not have a material impact on results, because the difference in sample duration calculated by either approach is typically orders of magnitude smaller than the sample duration required to get representative statistics from rainflow counting.
We have made this change to make it easier to check and verify OrcaFlex fatigue damage calculations against offline calculations.
User interface
- Model drawing can now be customised on a per-view basis. This is achieved by defining view filters to control the drawing properties of individual objects or object types. This includes global drawing elements such as global axes, view axes, scale bar, etc., in addition to axes and labels for individual objects. Filters use regular expression pattern matching to provide fine-grained control over the objects or object types that are matched by the filter. OrcaFlex provides tools to allow you to test your patterns. Filters are linked to each 3D view so you can control each view individually. They are saved within a workspace file but any filter can also be exported to a file for reuse. We also provide a series of view filter examples.
-
OrcaFlex files can contain references to external files. Sometimes, when files or folders are renamed, these references can be broken. Broken references to external files can prevent OrcaFlex from opening files. In order to help users deal with this, OrcaFlex will now prompt the user to repair any broken references to external files.
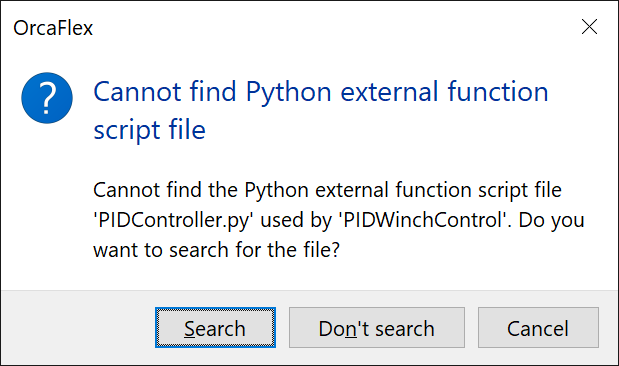
This functionality was previously implemented for time history files, but is now offered for all types of external file reference.
If you have a lot of files that need to be repaired in this way, this can be automated using the API. For instance, in Python this is done using correctExternalFileReferencesHandler.
- When editing data, it is now possible to move rows up or down within a table using ALT + ↑ and ALT + ↓.
- Auto suggest features in the user interface are now more widespread, and have improved functionality. Auto suggest was previously only available for certain stand-alone text controls that were used to specify file names. Now, auto suggest is available for text fields in grid controls. Additionally, auto suggest for file names is now aware of relative paths. If you start typing a relative path, you will be offered suggestions relative to the relevant parent file.
- A references report has been added which lists all instances where one object refers to another object. This can be displayed by clicking the Model | Show references report menu item. It displays, in a spreadsheet, a list of all references between objects in the model.
- Workspaces are now saved in a YAML format. Previously these were saved as INI files. The files are still saved using the
.wrk extension. Existing INI format workspace files are still understood by OrcaFlex so there should be no discernible change in behaviour from the user perspective. However, if you are processing these files outside of OrcaFlex, then this change may impact you. The new YAML format is much easier to work with, both manually in a text editor, and programmatically.
- Likewise, custom replays are now saved in a YAML format. Previously these were saved as INI files. The files are still saved using the
.txt extension. Existing INI format custom replay files are still understood by OrcaFlex so there should be no discernible change in behaviour from the user perspective. However, if you are processing these files outside of OrcaFlex, then this change may impact you. The new YAML format is much easier to work with, both manually in a text editor, and programmatically.
- The all objects data form now presents data for stacked 6D buoys.
- The model browser has a new action that allows you to sort selected objects by name, into either ascending or descending order.
- A new preference named display full file name in window caption has been added that determines how OrcaFlex displays the current file name in the main window caption. If the full file name is displayed (i.e. when the preference is checked), it may be truncated awkwardly, especially with very deep directory structures. If the preference is not checked, then only the final file name part of the full path is displayed. The full path to the file is always available using File | Properties.
- A new menu item, File | Copy to clipboard, has been added. This allows you to copy the following items to the clipboard as text: the name of the current file, the full path of the current file, and the directory which contains the current file.
External function examples
Previously our external function examples were installed alongside the program files, and also made available on our website. The documentation of these examples was provided in a separate PDF document. We have now integrated the external function examples into our OrcFxAPI documentation. The examples, including source code, can be downloaded directly from the OrcFxAPI documentation. The example content has been reviewed and in particular the native external function examples have been overhauled significantly. Previously these were written in C, but they are now written in C++ which makes the code significantly simpler. The examples can be found here:
OrcFxAPI (OrcaFlex programming interface)
- OrcaFlex now supports Python 3.9 and later. Older Python versions are now past their end of life, and so are no longer supported.
- In previous versions it was not permitted to explicitly import the
OrcFxAPI Python module in your embedded Python code, i.e. Python external functions, post calculation actions, user defined results etc. Starting with this version, there are now a number of scenarios where this is now permitted. Full details are provided in the Python API documentation.
- The function C_UseCalculatedPositionsForStatics has been extended to allow a simulation time to be specified. Previously, if the function was called after a time domain dynamic simulation, the calculated positions used were those from the latest calculated time. The extension of this function allows calculated positions from arbitrary points in a time domain dynamic simulation. This extension means that the API now matches the functionality that was already available in the user interface. The Python and MATLAB analogues,
UseCalculatedPositions, have also been extended.
- Functions C_SavePanelMesh and C_SavePanelMeshMem have been added to create panel mesh files from an array of panels. At the moment these functions can only be used to create WAMIT GDF files. This functionality can also be accessed from the Python and MATLAB interfaces. Together with the existing functionality for reading panel mesh files, this new functionality makes it possible to perform simple modifications to meshes such as converting between units systems, scaling, etc.
- The connections report can now be exported using the C_SaveSpreadsheet function. From Python and MATLAB this can be achieved using the
SaveConnectionsReport method.
- The functions which output model views can now be used to replicate the show trails feature of OrcaFlex replays. This is enabled using the
DrawTrails member of the TViewParameters structure, or the analogous structures in the Python and MATLAB interfaces.
- A new function, C_CreateBitmapCanvasClone, has been added to provide an alternative way to create a bitmap canvas. The new function accepts another bitmap canvas as an argument, and the newly created canvas is initialised with the existing image in the canvas passed to the function. This is intended to make it quicker to produce multiple images that share common frames, for example when creating an image using replay trails. The Python and MATLAB analogues,
BitmapCanvas and ofxBitmapCanvas, respectively, have been extended to offer this functionality.
- The expanded state of browser groups can set using a new boolean property named
Expanded.
Bug fix
- The solve coupled systems line statics step 2 option may have resulted in a stack overflow error for very large models with complex interconnectivity between objects.
This bug is fixed in version 11.6a.
New in version 11.5f
Python
Python external functions, post calculation actions and user defined results now support the latest version of Python, version 3.14.
Bug fixes
- When solving in the frequency domain using low frequency, combined linearisation solution frequencies, OrcaFlex initially performs a wave frequency solve that contributes to the quadratic drag linearisation. If a vessel type included other damping, that was solely calculated from primary wave frequency motion, then the vessel type's linear damping coefficients erroneously did not contribute to this initial wave frequency solve. This bug did not affect the vessel type's quadratic damping coefficients, nor other damping applied to low-frequency or total motion. Additionally, stand-alone wave or low-frequency solution modes were not impacted by this bug.
- When reading amplified drag coefficients from a SHEAR7
.plt file which contains duplicate values for x/L, no error was being raised. OrcaFlex would continue to process the file, with undefined behaviour. OrcaFlex models using fine segmentation can generate x/L values that have spacing smaller than the precision available in the SHEAR7 output file, which in turn can result in duplicate x/L values.
- Text data files which specify both the pitch controller and the imposed motion consistent with solver data could fail to load, reporting a change not allowed error.
- For modeless data forms, undo actions were not correctly recorded when a data form was closed by the next or previous action, or when using the edit other object context menu item.
- The decouple lateral and axial friction line-seabed contact option was not being inherited by a line's stiffener attachments. Lateral and axial friction were always treated as coupled for stiffeners.
- The apply contact forces at centreline line-seabed contact option was not being inherited by a line's stiffener attachments. Contact forces were always being applied at the contact point for stiffeners.
- The bespoke seabed contact properties defined by a line's seabed sections were not being inherited by its stiffener attachments.
- Changes made to the contents pressure reference Z level of a line had no effect in a restart analysis. The reference Z value was always inherited from the parent model.
- Results at some nodes may have been erroneously omitted from line feeding range graphs because OrcaFlex incorrectly viewed the nodes as belonging to growing or shrinking segments.
- Running a restart analysis in which an object's connection is changed from one line to another may have resulted in an access violation error. This would happen if the object was originally connected to a node whose node number exceeded the number of nodes on the new line.
- Turning on hysteretic stiffness for nodes that were previously inactive in a chain of restart analyses may have resulted in an access violation error.
- The turbine rotor aero Ct and Cp results would fail with an invalid floating point operation error if the air density was zero.
These bugs are fixed in version 11.5f.
New in version 11.5e
Bug fix
- In version 11.5d only, it was not possible to assign variable data sources to variable data items in the GUI.
This bug is fixed in version 11.5e.
New in version 11.5d
Bug fixes
- Running models with line feeding would sometimes result in an access violation error when the range of the ramping zone was far from the zero of simulation time.
- Running a frequency domain simulation that contained an indirectly solved constraint with no out-frame connection resulted in an unexpected program error.
- Following a frequency domain simulation, the y-component of the line node acceleration was omitted from the list of available line result variables.
- Current vertical stretching was applied to the tabular current velocity field, but not the acceleration field. Current vertical stretching should be applied to both.
- The OrcaFlex spreadsheet did not handle additional data for turbine results which specify a clearance line name.
- Calculations (statics or dynamics) for exceptionally large models would sometimes result in an access violation error.
- Variation models or restart analyses loaded from text data files could sometimes load incorrectly for models containing lines that use the calculated from end positions option to determine their length and end orientations.
- In the frequency domain, the load associated with a change in the proportion wet of a surface piercing 3D buoy, due to wave elevation, was phased incorrectly.
- OrcaWave results for sectional bodies in a non-inertial units system, for example US units, were imported incorrectly into OrcaFlex. Specifically, the vessel type datum buoyancy load was imported incorrectly.
- The disturbed sea surface elevation associated with sea state RAOs may have been calculated incorrectly when the global Z coordinate of mean water level was non-zero. This issue would have affected linear wave components when sea state RAOs were interpolated on position, direction and period. This bug may have affected surface piercing calculations performed as part of the simulation.
- Requesting line solid contact force results would lead to an unexpected program error for protected line nodes whose contact diameters are greater than that of the corresponding stiffener line node.
These bugs are fixed in version 11.5d.
New in version 11.5c
Lines
Bug fixes
- Deleting a body from a multibody group in a variation model or restart analysis could have resulted in an unexpected program error.
- The edit data as text feature would fail to apply modifications to the model in some situations. This would happen for variation models or restart analyses with parent models in different folders from the child.
- When solving in the frequency domain, hydrodynamic effects below the seabed were not being suppressed for lines with a P-y model.
- The compound page of the line properties report was not being updated when the report relative to object was changed. Similarly, the line type properties report was not being updated when the contents density was changed.
- Prescribed motion vessels may have restarted from the wrong position when performing a mid-simulation restart analysis.
- Editing a current data set in the user interface may have triggered an access violation error after loading a variation model or restart analysis that had been saved in binary format.
- Mid-simulation restarts require a parent simulation file which includes time domain dynamic analysis. OrcaFlex was previously not enforcing this. So, if the parent simulation file was a static state simulation, then OrcaFlex would proceed with the restart, but the resulting analysis would have been invalid.
- The angular velocity and angular acceleration of a curvilinear constraint's out-frame would have been computed incorrectly when there were fewer than two free rotational degrees of freedom and the rotational motion of the out-frame (relative to the in-frame) was not confined to a straight line through the origin of the rotational coordinate space parametrised by $Rx$, $Ry$ and $Rz$. A necessary, but not sufficient, condition to trigger the bug was that there was more than one non-zero component of rotation.
- Calculating time domain panel pressure results may have triggered an invalid multidimensional array arguments error if the corresponding OrcaWave model included only one wave heading.
- Restart analyses restarting from a paused parent simulation may have failed to run if they contained either winches or prescribed motion vessels.
- Restart analyses with line feeding could occasionally report a spurious insufficient inactive line has been defined warning.
- External functions which extract seabed normal resistance results could fail with an access violation error.
- Importing full QTFs from OrcaWave could fail with an error message that the full QTFs contain an unexpected wave frequency.
- Earlier 11.5 versions could sometimes report stiffener lines should have an inner contact diameter that is greater than the outer contact diameter of the protected line warnings for stiffeners whose inner contact diameter was not greater than the protected line outer contact diameter.
- Line segments could be drawn with excess length in shaded graphics. This incorrect segment extension only appeared for line segments that were both drawing slug flow and drawing contact. Only drawing is affected by this issue.
These bugs are fixed in version 11.5c.
New in version 11.5b
Bug fix
- If OrcaFlex could not find a license at startup, it would report an access violation error instead of an informative error message.
This bug is fixed in version 11.5b.


